Whether you have any questions, or wish to get a quote for your project, or require further information about what we can offer you, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Contact us Need a reliable software development partner?
S3Corp. offers comprehensive software development outsourcing services ranging from software development to software verification and maintenance for a wide variety of industries and technologies
Software Development Center
Office 146
3rd floor, SFC Building, 146E Nguyen Dinh Chinh, Phu Nhuan Ward, HCMC
Tien Giang (Branch)
1st floor, Zone C, Mekong Innovation Technology Park - Tan My Chanh Commune, My Phong Ward, Dong Thap Province
_1746790910898.webp?w=384&q=75)
_1746790956049.webp?w=384&q=75)
_1746790970871.webp?w=384&q=75)

Why Outsource to Vietnam

Insights
Table Of Content
Introduction
Industry Reviews
Why Companies Outsource to Vietnam
Vietnam's Talent Pool
Cost Comparison: Vietnam vs. India / Philippines / Eastern Europe
Software Development Hubs in Vietnam
Strengths That Make Vietnam Competitive
Challenges to Consider
How to Outsource to Vietnam Successfully
Top Types of Projects Commonly Outsourced to Vietnam
Leading Software Outsourcing Companies in Vietnam
Conclusion
FAQs
Vietnam combines skilled developers, competitive pricing, and reliable delivery for global software outsourcing. Explore talent pools, cost comparisons, and how to start your project.
27 May 2020
Software outsourcing services have recently gained global popularity. Companies are employing these services for both cost-savings and time saving as well as a multitude of other benefits.
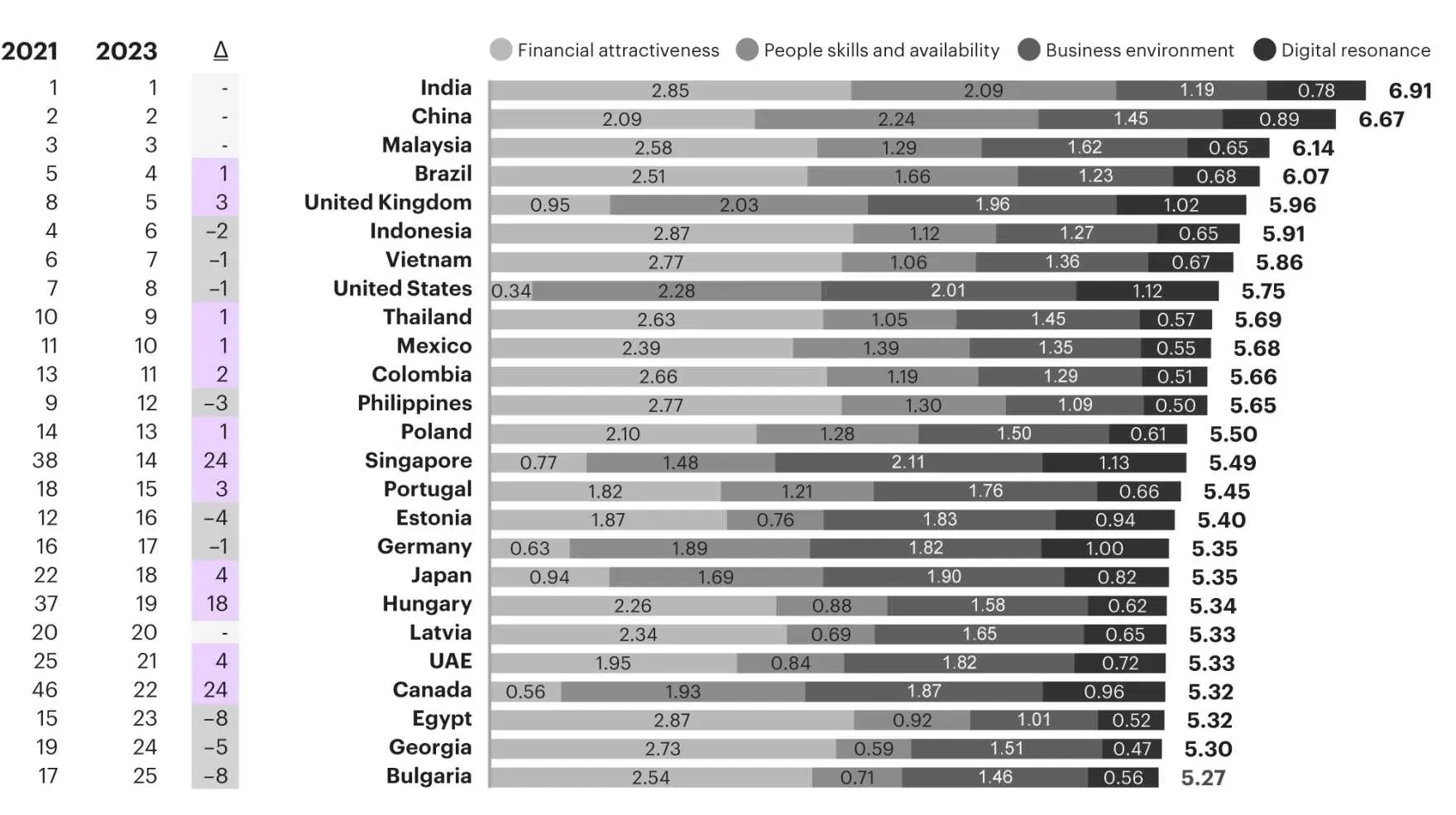
India and China, have established themselves as leaders in the field. However, the picture of outsourcing services has changed. Several new countries, including Vietnam, are becoming the rising stars in the IT outsourcing market.
Indeed, Vietnam has become a powerhouse in software outsourcing. Companies from the United States, Japan, Australia, and Europe now turn to Vietnam for skilled developers, strong technical delivery, and competitive costs. The country offers what businesses need: experienced engineering teams, modern technology adoption, and pricing that makes sense.
Software outsourcing Vietnam delivers real advantages. You get access to a workforce trained in current programming languages and frameworks. You benefit from a stable business climate with supportive government policies. You work with teams that understand global quality standards. These factors explain why Vietnam outsourcing has grown rapidly over the past decade.
When compared to established nations like India and China, Vietnam's outsourcing industry appears to be in its early stages. This, however, will not prevent the fast growth of Vietnam's IT outsourcing industry. The industry is predicted to generate $694.80 million in revenue in 2024, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.23% over the next five years, reaching $1.24 billion in 2029.
A.T. Kearney-a leading global management consulting firm established in 1926. In their 2023 Global Services Location Index™ (GSLI) report, which identifies the top 50 locations providing IT, BPO, and voice services; the report shows Vietnam, ranked 7th, continues to shine as a leading Asian outsourcing destination. The presence of major global tech companies solidifies its position as a digital hub, driving the nation's commitment to upskilling its workforce. As highlighted in the GSLI report, Vietnam is recognized among the top 10 countries excelling in IT, BPO, and voice services, further cementing its role in the global outsourcing landscape.
Gartner- a global technology research and advisory firm providing technology-related insights for businesses., Gartner identified the top 10 Locations for Services in APAC, including Vietnam.
Besides that, Forbes has highlighted Vietnam's rise as a favorable outsourcing destination, noting its rapid progress in digital services and competitive developer rates. Companies can cut costs by 30% to 50% on IT jobs compared to India and similar places. Vietnamese coders charge about $20 to $40 an hour, while U.S. developers ask for $100. This cost advantage, combined with Vietnam's skilled workforce, positions the country as an ideal choice for companies seeking cost-effective development solutions.
 Why Companies Outsource to Vietnam
Why Companies Outsource to VietnamVietnam has over 500,000 IT professionals. About 50,000 new technology graduates enter the workforce each year. This talent pool keeps growing as universities expand STEM programs and coding bootcamps multiply across major cities.
The median age of developers is under 30. Young engineers bring energy, quick learning ability, and familiarity with modern development practices. Many have experience with agile methodologies, cloud platforms, and DevOps practices from their first jobs.
Vietnam software development teams work with current technologies. Popular stacks include React, Angular, and Vue.js for front-end development. Node.js, Golang, Python, and Java dominate back-end work. Mobile developers use React Native, Flutter, Swift, and Kotlin.
Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are standard tools. Vietnamese developers also work with Docker, Kubernetes, and microservices architectures. AI and machine learning projects increasingly use TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
Vietnam developer rates remain competitive compared to Western markets. Hourly rates range from $25 to $50 for mid-level developers. Senior engineers and architects charge $50 to $80 per hour. These rates are 60-70% lower than comparable talent in the United States or Western Europe.
A full development team of five people costs roughly $15,000 to $25,000 monthly. Compare this to $50,000 or more for an equivalent team in San Francisco or London. The math makes sense for startups managing runway and enterprises optimizing budgets.
Political stability supports long-term partnerships. The Vietnamese government actively encourages foreign investment in technology. Free trade agreements with major economies reduce barriers. Intellectual property protections have strengthened significantly over recent years.
Special economic zones offer additional benefits. Companies can establish legal entities relatively easily. Banking infrastructure supports international transactions. These practical considerations matter when choosing an offshore development location.
The digital economy in Vietnam grows approximately 15% annually. E-commerce, fintech, and logistics technology drive demand for software services. This domestic market pushes developers to build real products, not just complete outsourced projects.
Internet penetration exceeds 70%. Smartphone usage is nearly universal among urban populations. Developers understand mobile-first design because they live in a mobile-first society. This perspective benefits international clients building consumer applications.
Major technology companies have established offices in Vietnam. Samsung employs thousands of engineers. Intel maintains research facilities. Google, Microsoft, and others have expanded their presence. This foreign investment validates the quality of the local workforce.
These companies also train developers in enterprise standards. Engineers who have worked for global corporations bring that experience to Vietnam software companies serving international clients. The knowledge transfer strengthens the overall ecosystem.
Over 500,000 IT professionals work across software development, testing, infrastructure, and support roles. Ho Chi Minh City accounts for about 40% of this workforce. Hanoi represents another 35%. Da Nang and other cities contribute the remaining 25%.
The IT outsourcing Vietnam sector employs roughly 200,000 people directly. These developers work primarily on international projects for clients in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific markets. The remaining workforce serves domestic companies or foreign-invested enterprises with local operations.
JavaScript dominates with the highest number of proficient developers. Java maintains strong popularity, especially for enterprise applications. Python grows rapidly due to increasing demand for data science and AI projects.
C# remains common for legacy system maintenance and .NET projects. PHP still serves many web applications. Go and Rust are gaining traction for systems programming and blockchain projects. Swift and Kotlin handle mobile development for iOS and Android respectively.
Web development represents the largest skill category. Developers build responsive websites, progressive web apps, and complex single-page applications. Experience with REST APIs, GraphQL, and WebSocket implementations is common.
Mobile app development is the second-largest category. Teams deliver native iOS and Android apps plus cross-platform solutions. Push notifications, in-app purchases, location services, and device integrations are routine requirements.
Cloud architecture and DevOps form a growing specialty. Engineers design AWS and Azure deployments, configure CI/CD pipelines, and manage containerized applications. Infrastructure-as-code using Terraform or CloudFormation is standard practice.
AI and machine learning represent emerging strength. Data scientists build recommendation engines, image recognition systems, natural language processing tools, and predictive models. Computer vision projects use OpenCV and deep learning frameworks.
Vietnam graduates approximately 50,000 IT students annually from universities and technical colleges. Top institutions include Vietnam National University, Hanoi University of Science and Technology, and Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology.
Coding bootcamps supplement formal education. Programs lasting 3-6 months teach practical skills in web development, mobile apps, and data analysis. Many graduates from non-technical backgrounds successfully transition into software careers through these programs.
International certifications are common. Developers pursue AWS certifications, Google Cloud credentials, and Microsoft Azure qualifications. Scrum Master and Product Owner certifications indicate familiarity with agile methodologies.
Mid-level developers with 3-5 years of experience form the largest segment of the workforce. These engineers handle most day-to-day development tasks competently. They understand design patterns, testing practices, and code review processes.
Senior developers and architects with 8-12 years of experience are available but require more careful recruitment. They lead technical decisions, design system architectures, and mentor junior team members. Their experience often includes working directly with international clients.
Technical leads and CTOs with 15+ years of experience exist but are in high demand. These professionals typically work for established Vietnam software companies or have founded their own firms. Securing their time requires competitive compensation and interesting technical challenges.
Vietnam software development outsourcing offers competitive pricing. Junior developers cost $20-$30 per hour. Mid-level developers range from $30-$45 per hour. Senior developers and specialists charge $50-$80 per hour.
India maintains similar or slightly lower rates. Junior developers start at $15-$25 per hour. Mid-level talent costs $25-$40 per hour. Senior developers charge $45-$70 per hour. However, attrition rates in India run higher, which can disrupt project continuity.
The Philippines focuses more on customer support and BPO services than pure software development. Developer rates range from $25-$50 per hour. The talent pool for complex engineering work is smaller compared to Vietnam.
Eastern Europe (Ukraine, Poland, Romania) charges more. Junior developers cost $30-$40 per hour. Mid-level developers range from $45-$65 per hour. Senior developers exceed $80 per hour. Political instability in some regions adds risk.
A typical web application requiring 2,000 development hours illustrates the savings. In Vietnam, this project costs approximately $70,000-$90,000. The same project in the United States would cost $200,000-$300,000. European rates would reach $150,000-$200,000.
For ongoing maintenance and feature development, monthly savings compound. A dedicated team of five developers in Vietnam costs $15,000-$25,000 monthly. The equivalent team in Western markets runs $50,000-$80,000 monthly. Annual savings exceed $400,000.
These figures assume comparable quality and productivity. Experience shows that well-managed offshore development teams in Vietnam match or exceed onshore productivity when projects have clear requirements and regular communication.
The Vietnamese dong maintains relative stability against major currencies. The central bank manages exchange rates carefully to support export industries. Significant currency fluctuations are rare, which helps with budget planning.
Contracts typically specify payment in US dollars or euros. This practice eliminates currency risk for international clients. Vietnam software companies handle local currency conversion and accept the associated exchange rate exposure.
Small projects use teams of 2-3 developers plus a project manager. Monthly costs run $8,000-$15,000. These teams suit MVP development, simple websites, or mobile apps with limited functionality.
Medium projects deploy teams of 5-8 people including developers, QA engineers, and a project manager. Monthly costs range from $20,000-$35,000. These teams handle complex web applications, enterprise software modules, or feature-rich mobile apps.
Large projects require teams of 10-20+ people with multiple specializations. Monthly costs exceed $50,000. These teams build complete platforms, migrate legacy systems, or develop comprehensive enterprise solutions.
Ho Chi Minh City dominates software outsourcing Vietnam. About 200,000 IT professionals work in the city. The majority of Vietnam software companies maintain headquarters or major offices here.
District 1, District 3, and Binh Thanh District concentrate development centers. Modern office buildings house hundreds of software companies. Co-working spaces provide alternatives for startups and small teams.
The city offers the deepest talent pool across all skill levels and specializations. Companies find front-end developers, mobile specialists, DevOps engineers, and data scientists more easily than in other locations. Recruitment timelines are shorter.
Cost of living remains moderate compared to other Asian tech hubs like Singapore or Hong Kong. Developer salaries reflect this reality, contributing to the competitive rates international clients enjoy.
Hanoi serves as the political capital and second-largest technology center. Approximately 175,000 IT professionals work in the city. Several top engineering universities feed the talent pipeline.
The city attracts developers interested in more traditional corporate environments. Many large Vietnam software companies and foreign-invested enterprises maintain significant operations in Hanoi. Samsung, Intel, and other multinational corporations employ thousands of engineers.
Developers in Hanoi often demonstrate strong fundamentals due to rigorous university programs. The city produces excellent talent for complex algorithmic work, systems programming, and research-oriented projects.
Developer rates in Hanoi roughly match Ho Chi Minh City. Slight variations exist but rarely affect project budgets significantly. The choice between cities usually depends on existing company presence or specific talent requirements.
Da Nang has emerged as a third development hub. About 25,000-30,000 IT professionals work in the city. The number grows steadily as companies seek alternatives to crowded major cities.
The coastal location offers lifestyle advantages. Beautiful beaches, cleaner air, and less traffic congestion appeal to developers considering relocation. Several Vietnam software companies have opened offices specifically to tap this market.
Costs in Da Nang run slightly lower than the two major cities. Junior and mid-level developers are abundant. Senior talent is growing but requires more lead time to recruit. The city suits teams focused on web development, mobile apps, and standard enterprise work.
Government incentives encourage technology investment. Software parks offer favorable lease terms. The local administration actively supports the IT outsourcing Vietnam industry with infrastructure improvements and skills training programs.
Vietnam software development outsourcing delivers consistent quality. Developers follow international coding standards. Code reviews, automated testing, and continuous integration are standard practices at professional firms.
Many Vietnam software companies hold ISO certifications, CMMI Level 3 or higher ratings, and industry-specific compliance credentials. These certifications require documented processes and regular audits. They provide assurance to clients concerned about quality management.
Bug rates and defect density metrics compare favorably to other outsourcing destinations. Well-run teams maintain test coverage above 80%. Production incidents remain low when proper QA processes are followed.
Vietnamese culture emphasizes education, hard work, and professional dedication. Developers take pride in their craft. Meeting deadlines and delivering on commitments matter deeply. This cultural trait translates to reliable project execution.
Work hours align with international standards. Typical schedules run Monday through Friday with reasonable expectations. Overtime occurs but is not systematically exploited. Sustainable pace prevents burnout and maintains productivity.
Team stability contributes to project success. Developers who feel respected and fairly compensated stay with projects long-term. This continuity preserves knowledge and reduces onboarding overhead.
Vietnam software companies quickly adopt new frameworks, tools, and methodologies. Agile and Scrum are widely understood and practiced. Kanban boards, daily standups, and sprint retrospectives are routine.
Security practices follow OWASP guidelines. Developers understand common vulnerabilities and how to prevent them. Secure coding training is standard for teams working on financial services or healthcare projects.
Cloud-native development is the norm for new projects. Microservices, containers, and serverless architectures are familiar concepts. Teams adapt to client technology preferences without lengthy training periods.
Vietnamese professionals demonstrate strong cultural adaptability. They work successfully with clients from North America, Europe, Australia, and other Asian countries. Business etiquette aligns with international norms.
Communication style tends toward politeness and consensus-building. This approach works well in collaborative relationships. Developers ask clarifying questions rather than making assumptions. They flag potential issues early rather than hiding problems.
Time zone overlap with Asian markets is excellent. Overlap with European time zones is reasonable for morning meetings. Working with US time zones requires flexibility but many teams accommodate evening calls or adjusted schedules for critical project phases.
Developer turnover in Vietnam runs lower than India or the Philippines. Annual attrition rates of 10-15% are common at well-managed firms. This compares favorably to 20-30% attrition seen in other markets.
Lower turnover means knowledge retention. Developers who work on a project for 12-18 months understand the codebase deeply. They provide more valuable contributions and require less oversight.
Companies invest in employee retention through competitive salaries, career development programs, and positive work environments. Clients benefit from these investments through team stability and project continuity.
English skills vary across the Vietnamese workforce. Developers in tier-one cities generally communicate effectively in written English. They read technical documentation, understand requirements, and write clear commit messages and comments.
Spoken English presents more challenges. Accents can require adjustment periods. Complex verbal discussions may need repetition or written summaries. Video calls work better than phone calls for important conversations.
Technical English is usually stronger than casual conversation. Developers comfortable discussing API design or database optimization may struggle with small talk. This gap narrows with exposure and practice.
Mitigation strategies work well. Use written communication for detailed requirements. Record video calls for reference. Employ bilingual project managers when necessary. These approaches enable effective collaboration despite language differences.
Vietnam operates in GMT+7. This creates significant time differences with North American clients. When it's 9 AM in New York, it's 9 PM in Ho Chi Minh City. When it's 9 AM in San Francisco, it's 12 AM (midnight) in Vietnam.
European time zones are more manageable. When it's 9 AM in London, it's 4 PM in Vietnam. This allows for afternoon meetings on the European side and morning meetings on the Vietnamese side.
Asian-Pacific clients enjoy excellent alignment. Japan is two hours ahead. Singapore shares the same time zone. Australia has minimal time difference. These regions experience no time zone challenges.
Successful approaches include asynchronous communication as the default mode. Document decisions in writing. Use project management tools that show progress visibly. Schedule weekly sync meetings at times acceptable to both sides. Some Vietnamese teams work partially shifted schedules to create more overlap.
Like all outsourcing arrangements, Vietnam software development outsourcing works best with well-defined requirements. Vague or constantly changing specifications create confusion and rework. The physical distance and cultural differences amplify this challenge.
Detailed user stories with acceptance criteria help tremendously. Wireframes and mockups prevent misunderstandings about UI expectations. API specifications clarify integration points. Database schemas define data structures precisely.
Iterative delivery with frequent feedback loops catches issues early. Two-week sprints with demo sessions allow course corrections before too much work diverges from expectations. This agile approach compensates for imperfect initial requirements.
Ad-hoc communication works poorly across distance and time zones. Structured communication becomes essential. Daily written updates, weekly video meetings, and monthly reviews create predictable touchpoints.
Documentation matters more in distributed teams. Architecture decision records capture why choices were made. README files explain project setup. Confluence or similar wikis organize knowledge. These artifacts help new team members onboard and serve as reference for everyone.
Communication tools should be standardized. Slack or Microsoft Teams for chat. Jira for task tracking. GitHub or GitLab for code. Zoom or Google Meet for video. Agreeing on the stack upfront prevents scattered conversations across multiple platforms.
Document what you want to build before approaching vendors. Create a product requirements document or a detailed scope statement. Include functional requirements, non-functional requirements, and constraints.
Functional requirements describe what the software should do. "Users can create an account with email and password" is a functional requirement. "The system processes credit card payments" is another example.
Non-functional requirements define quality attributes. "The application loads in under 2 seconds" specifies performance. "The system maintains 99.9% uptime" defines reliability. "All data transfers use TLS encryption" addresses security.
Constraints limit the solution space. "Must integrate with Salesforce" is a constraint. "Must run on AWS" is another. "Must support 50,000 concurrent users" constrains the architecture. Clear constraints prevent wasted effort on unsuitable approaches.
Visual aids help enormously. Wireframes show screen layouts. User flows diagram navigation paths. Entity-relationship diagrams illustrate data models. Architecture diagrams depict system components.
Research potential Vietnam software companies thoroughly. Review their website and case studies. Check their technology stack matches your needs. Verify they have experience in your industry or application type.
Request client references and actually contact them. Ask about communication quality, technical capability, and problem resolution. References reveal how companies handle challenges, which matters more than glossy marketing materials.
Evaluate portfolios critically. Look for projects similar in complexity to yours. Assess code quality if samples are available. Check if live applications perform well and have good user experiences.
Consider company size appropriately. Large firms offer more resources and formal processes. Small firms provide flexibility and potentially more attention. Match the company profile to your project needs and preferred working style.
Conduct technical interviews with proposed team members. Verify their skills match what the company claims. Assess communication ability during these conversations. Meet the specific people who will work on your project, not just sales representatives.
Establish communication cadence upfront. Daily standups at an agreed time work for most projects. Weekly sprint reviews demonstrate progress. Bi-weekly retrospectives enable process improvements.
Designate primary contacts on both sides. A single point of contact on your side and a project manager on the vendor side streamline information flow. These individuals ensure questions get answered and decisions get communicated.
Choose communication channels explicitly. Real-time chat for quick questions. Email for formal communications and documentation. Video calls for complex discussions. Project management tools for task tracking. Everyone should know which channel to use for which purpose.
Define response time expectations. Four hours for urgent issues. Twenty-four hours for normal questions. These agreements prevent frustration when responses seem slow due to time zone differences.
Document important decisions in writing. After a video call where key choices were made, send a summary email. This practice creates a record and allows correction of any misunderstandings before implementation begins.
Time and materials suits projects with evolving requirements. You pay for hours worked. This model provides flexibility to change direction. It requires trust and good oversight since costs can grow.
Fixed price works for well-defined projects with stable scope. The vendor quotes a total price for delivered functionality. This model transfers risk to the vendor. It requires very detailed specifications upfront and disciplined change control.
Dedicated team operates like staff augmentation. You pay a monthly fee for a team of specified size and composition. The team works exclusively on your projects. This model suits ongoing development needs and provides predictability.
Hybrid models combine elements. Perhaps core features are fixed price but enhancements are time and materials. Or a dedicated team with a monthly cap. Custom arrangements can match your specific situation.
Establish intellectual property ownership in the contract before work begins. Standard practice gives clients full ownership of all code, designs, and documentation created during the project.
Non-disclosure agreements protect confidential information. Both parties should sign NDAs covering business information, technical details, and customer data. These agreements should survive contract termination.
Code repositories should be under your control. Use your GitHub or GitLab account. Grant the vendor team access as needed. This ensures you maintain the code even if the relationship ends.
Source code escrow provides additional protection for critical systems. The vendor deposits code regularly with a third-party escrow agent. You can access it if the vendor fails to perform or goes out of business.
Data security provisions should specify how your data is handled. Where is it stored? Who has access? How is it protected? What happens to it after the project ends? Clear answers prevent security gaps.
Web applications form the largest category of outsourced projects. Teams build customer portals, internal management systems, e-commerce platforms, and SaaS products. Technologies include React, Angular, Vue.js for front-end work. Node.js, Python Django, Ruby on Rails, PHP Laravel, and Java Spring for back-end development.
Content management systems are common requests. Teams implement WordPress, Drupal, or headless CMS solutions. Custom CMS development occurs when off-the-shelf solutions do not fit requirements.
Progressive web apps combine web and mobile advantages. These applications work offline, send push notifications, and install on home screens. They cost less than native mobile apps while providing much of the same functionality.
Native iOS and Android development remains popular. Businesses want applications that fully utilize platform capabilities and provide optimal performance. Swift and Kotlin are the primary languages.
Cross-platform development using React Native or Flutter reduces costs and development time. A single codebase deploys to both platforms. Performance suffices for most business applications. Complex games or apps with intensive graphics usually require native development.
Backend-for-mobile development provides the APIs and services mobile apps consume. These projects include authentication systems, data synchronization, push notification infrastructure, and payment processing integration.
Quality assurance outsourcing helps companies lacking dedicated QA resources. Manual testing covers functional testing, usability testing, and exploratory testing. Testers follow test plans and document defects carefully.
Automated testing creates scripts that run repeatedly. Selenium, Cypress, and similar tools automate browser-based testing. Appium handles mobile app automation. These scripts catch regressions when code changes.
Performance testing evaluates system behavior under load. Load testing simulates expected usage levels. Stress testing pushes systems beyond normal capacity to find breaking points. These tests identify bottlenecks before production deployment.
Security testing finds vulnerabilities. Penetration testing simulates attacks. Code analysis tools scan for common security flaws. These activities are essential for applications handling sensitive data or financial transactions.
Moving legacy applications to cloud platforms is a common project type. Teams assess existing systems, plan migration strategies, refactor applications as needed, and execute the move. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are the primary targets.
Lift-and-shift migration moves applications with minimal changes. Virtual machines in the cloud replace physical servers. This approach is fastest but does not fully exploit cloud advantages.
Re-platforming modifies applications to use managed services. Replacing a self-managed database with RDS or Azure SQL Database is an example. These changes improve reliability and reduce operational burden.
Refactoring redesigns applications as cloud-native systems. Monoliths become microservices. Applications use auto-scaling, managed queues, and serverless functions. This approach maximizes cloud benefits but requires more effort.
Recommendation engines suggest products, content, or connections. These systems analyze user behavior and preferences. Collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and hybrid approaches are common techniques.
Image recognition identifies objects, faces, or scenes in photos and videos. Applications include product identification, document processing, and security monitoring. Convolutional neural networks power most image recognition systems.
Natural language processing analyzes text and speech. Sentiment analysis determines if feedback is positive or negative. Chatbots answer customer questions. Text classification routes support tickets to appropriate teams.
Predictive models forecast future outcomes. Customer churn prediction identifies at-risk subscribers. Demand forecasting optimizes inventory. Fraud detection flags suspicious transactions. These models use historical data to learn patterns.
Online stores remain in constant demand. Teams build both B2C and B2B e-commerce platforms. Shopping cart functionality, product catalogs, payment gateway integration, and order management are core features.
Multi-vendor marketplaces are more complex. They support multiple sellers, handle commission calculations, provide seller dashboards, and manage dispute resolution. Examples include platforms similar to Amazon, Etsy, or Alibaba.
Subscription and recurring billing systems handle membership sites, SaaS products, and subscription boxes. They manage trial periods, automatic renewals, plan changes, and dunning processes for failed payments.
The best software outsourcing companies Vietnam market includes firms with proven track records, strong technical capabilities, and reliable delivery. When evaluating options, look for companies with relevant experience, clear communication practices, and transparent pricing.
Established firms typically hold quality certifications like ISO 9001 or CMMI Level 3. They maintain security certifications such as ISO 27001 for information security management. These credentials indicate structured processes and commitment to standards.
Client testimonials and case studies provide insight into actual experiences. Companies should share examples of completed projects with measurable results. References from clients in your industry or building similar applications carry particular weight.
Technical expertise should match your needs. A company strong in mobile development may not excel at AI projects. A firm experienced in fintech may lack healthcare compliance knowledge. Verify the specific skills required for your project exist within the team.

S3Corp., founded in 2007, has become a leading software development company in Vietnam, earning global trust for its quality and professionalism. With 16+ years of experience, it has executed 450+ projects across various domains like security, finance, health, and more, showcasing its expertise.
Partnered with industry leaders like Microsoft, Sitecore, Magento, Umbraco Sitecore, GrowVC, Startup Commons, Amazon, S3Corp. offers innovative software solutions using cutting-edge technologies to meet client needs.
- Proven Excellence: Over 450+ successful projects globally in various industries
- Quality Delivery: Commitment to delivering exceptional solutions on time and within budget.
- Collaborative Solutions: Tailored solutions addressing unique business needs.
- Skilled Team: Certified engineers with international experience in various technologies.
- Focus on Knowledge: Continuous learning programs to stay updated with tech advancements.
- Security: Stringent policies safeguard intellectual property and client data.
- Long-term Partnerships: Flexible methodologies and collaboration for project success.
- Scalability: Modern IT infrastructure supporting growth and scalability.
Embarking Success in Software Development with S3Corp.
S3Corp. is dedicated to guiding companies to accomplish their goals in software development. Our commitment is to provide our clients with innovative and top-notch software solutions that help them succeed.
If you are considering to build your project and want to look for a leading software development company, contact us now to get free consultancies from our expert team. We are eager to delve into your project specifics and provide a customized solution crafted to meet your distinct needs.
Vietnam delivers the combination global businesses seek when outsourcing software development: skilled engineers, reliable delivery, and competitive costs. The talent pool continues growing with 50,000 new graduates annually. Developer rates remain 60-70% below Western markets. Quality standards match international expectations.
The IT outsourcing Vietnam industry has matured significantly. Companies hold recognized certifications. Teams follow agile methodologies. Security practices meet compliance requirements. This professionalism supports successful partnerships.
Software development hubs in Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, and Da Nang provide access to hundreds of thousands of developers. Modern tech stacks, cloud platforms, and emerging technologies like AI are well represented. The workforce adapts quickly to new frameworks and tools.
Challenges exist but have proven solutions. English proficiency continues improving. Time zones require structured communication but do not prevent effective collaboration. Clear requirements and established processes enable distributed teams to succeed.
Outsourcing to Vietnam makes business sense for companies seeking to extend development capacity, access specialized skills, or control costs without sacrificing quality. The combination of competitive pricing, technical capability, and reliable delivery explains why more businesses choose Vietnam for software development partnerships.

Vietnam developer rates range from $25 to $80 per hour depending on experience level and specialization. A typical development team of five people costs approximately $15,000 to $25,000 per month. Fixed-price projects vary widely based on complexity but small web applications start around $20,000 while complex enterprise systems can exceed $200,000.
Most Vietnam software companies accommodate client time zones through flexible scheduling. Teams shift hours to create overlap for meetings. Asynchronous communication becomes the primary mode with daily written updates. Weekly video calls at mutually convenient times maintain alignment. Project management tools provide visibility into progress regardless of time differences.
Start by defining your project requirements clearly. Research potential Vietnam software companies through web searches, referrals, or platforms like Clutch. Contact 3-5 companies and discuss your project. Request proposals with timelines and pricing. Check references and evaluate portfolios. Select a partner and begin with a small pilot project or proof-of-concept to validate the relationship before committing to larger work.
Project duration depends on scope and complexity. Simple websites or mobile apps require 2-3 months. Medium-complexity applications take 4-6 months. Large enterprise systems need 8-12 months or longer. Ongoing product development operates in continuous cycles with new features releasing every few weeks or months.
Professional Vietnam software companies protect client IP through contracts specifying full client ownership of all work product. Non-disclosure agreements prevent information disclosure. Secure development practices protect code and data during development. Code repositories remain under client control. These protections, combined with Vietnam's strengthening IP laws, provide reasonable assurance for international clients.