Things You Can Do With 5G

Insights
Discover how 5G technology transforms mobile apps through ultra-fast speeds, millisecond latency, and edge computing. Learn real use cases, architecture changes, and development strategies for 5G-ready applications
04 Mar 2016
The fifth generation of wireless technology changes how mobile apps function. 5G networks deliver speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, reduce latency to under 10 milliseconds, and support millions of connected devices per square kilometer. These improvements shift what developers can build and how users interact with mobile applications.
Mobile apps no longer need to rely heavily on device processing power. With 5G, complex computations move to edge servers or cloud platforms while maintaining real-time responsiveness. A video editing app can render 4K footage in the cloud and stream results instantly. A multiplayer game can synchronize hundreds of players without noticeable lag. An augmented reality shopping app can overlay 3D product models on your living room in real time.
This article explains how 5G technology transforms mobile app development, from architecture changes to new use cases that were impossible on previous networks.
5G technology represents the fifth generation of cellular network standards. This wireless communication system operates on three spectrum bands: low-band (below 1 GHz), mid-band (1-6 GHz), and high-band millimeter wave (24-100 GHz). Each band offers different trade-offs between coverage area and data transmission speed.
The technology introduces three core improvements. First, data transfer speeds reach 10 to 20 Gbps in optimal conditions, compared to 4G's maximum of about 1 Gbps. Second, network latency drops from 50 milliseconds on 4G to as low as 1 millisecond on 5G networks. Third, device density increases dramatically, allowing networks to support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer versus 4G's limit of roughly 100,000 devices.
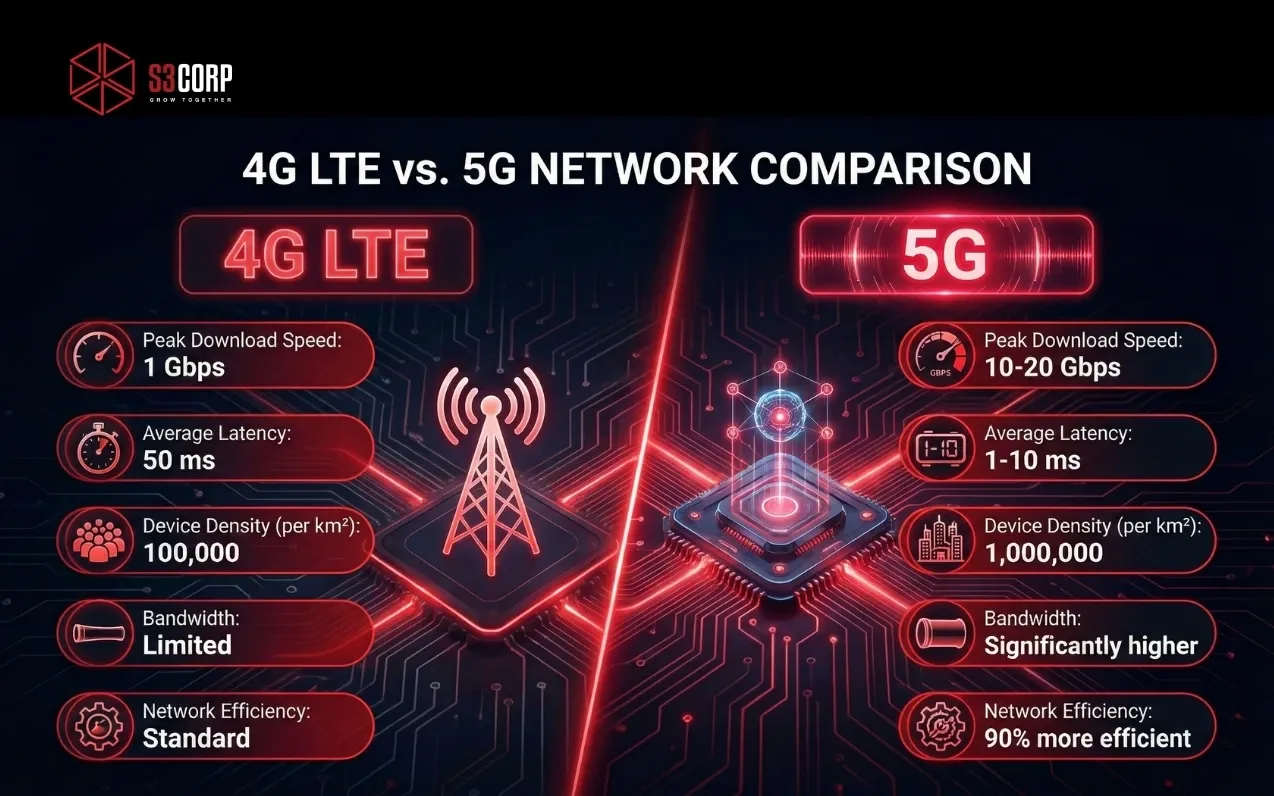 These specifications translate to practical changes. You can download a full-length movie in seconds. Video calls maintain quality even with dozens of participants. Apps respond to touch inputs without perceptible delay. Connected devices in smart buildings, factories, and cities communicate simultaneously without network congestion.
These specifications translate to practical changes. You can download a full-length movie in seconds. Video calls maintain quality even with dozens of participants. Apps respond to touch inputs without perceptible delay. Connected devices in smart buildings, factories, and cities communicate simultaneously without network congestion.
5G technology changes three fundamental aspects of mobile app performance and design.
Faster data streams eliminate waiting. Apps can pull high-resolution images, video content, and large datasets instantly. A real estate app displays 3D property tours without buffering. A medical imaging app loads CT scans in seconds instead of minutes. Streaming services deliver 4K or 8K video without quality reduction. This speed removes previous constraints on content richness and data volume.
Real-time interaction becomes standard across all app categories. Chat applications show typing indicators with zero delay. Collaborative editing tools reflect changes from multiple users instantly. Trading apps execute orders in milliseconds. Gaming apps sync player actions across continents without lag. The low latency of 5G networks means apps can build features that require instantaneous communication between devices, servers, and users.
Cloud dependency reduction sounds contradictory, but 5G actually makes cloud services more viable for tasks previously handled on-device. With fast connections and low latency, apps can offload processing to powerful cloud servers without users noticing the round trip. A photo editing app runs AI enhancement algorithms in the cloud but delivers results as quickly as if they ran locally. This approach saves battery life, reduces app size, and lets developers update features without requiring users to download new versions.
These improvements create opportunities for new app categories and features that couldn't exist on 4G networks. Edge computing for mobile apps becomes practical. Real-time mobile applications deliver experiences previously possible only on dedicated networks. Low-latency app architecture enables use cases in healthcare, industrial automation, and remote operation that require split-second timing.
 4 Ways 5G Technology Changes Mobile Apps
4 Ways 5G Technology Changes Mobile AppsAugmented reality apps transform with 5G mobile app development. Previous AR experiences struggled with tracking accuracy and object persistence because devices processed everything locally with limited power. 5G enables cloud rendering, where heavy computational work happens on remote servers with powerful GPUs while your phone simply displays the results.
Consider an AR furniture shopping app. On 4G, the app loads basic 3D models of chairs and tables stored in its local database. With 5G, the app streams photorealistic furniture models rendered in real time, complete with accurate lighting, shadows, and material textures. You see exactly how a leather sofa reflects light in your specific room conditions. The app processes room dimensions, lighting analysis, and 3D rendering on edge servers, delivering results to your screen in milliseconds.
Gaming apps gain capabilities that match console experiences. Multiplayer sync happens without noticeable delay, so competitive games remain fair regardless of player location. A racing game can sync the positions of 50 cars in real time. A battle royal game tracks hundreds of players across a large map. Cloud gaming services stream console-quality games to mobile devices, with user inputs processed so quickly that players don't notice the game runs remotely.
AR overlays for professional use cases become practical. Field service technicians view equipment schematics overlaid on machinery through phone cameras. Warehouse workers see picking instructions projected on shelves. Surgeons access patient data and 3D anatomical models during procedures. These applications demand rock-solid reliability and instantaneous updates, requirements that 5G networks fulfill.
Live data visualization apps can display information that updates by the second. Financial traders watch real-time market movements with sub-second data feeds. Sports fans track live statistics during games. Emergency responders monitor incident data from multiple sources simultaneously. The combination of high bandwidth and low latency means apps can present complex, constantly changing information without overwhelming networks or devices.
Edge computing for mobile apps moves processing closer to users while maintaining centralized intelligence. This architecture places compute resources at the network edge—in regional data centers or even at cell towers—rather than distant cloud facilities.
What moves from device to edge varies by application. Image recognition shifts to edge servers, allowing security apps to identify faces or objects without draining phone batteries. Natural language processing runs at the edge, enabling voice assistants to understand complex commands faster. Video transcoding happens at the edge, letting video apps adapt stream quality based on current conditions without device involvement.
Lower battery usage emerges as a major benefit. When your phone offloads intensive tasks to nearby edge servers, it consumes less power. A navigation app that processes traffic data and route optimization at the edge extends battery life significantly compared to performing these calculations locally. Video streaming apps that leverage edge caching reduce the energy needed to decode and display content.
Faster API responses occur because data travels shorter distances. An app requesting weather data from an edge server 50 kilometers away receives responses in 5-10 milliseconds. The same request to a cloud data center 5,000 kilometers away might take 100 milliseconds or more. For low-latency app architecture, this difference determines whether an app feels instantaneous or sluggish.
IoT mobile applications benefit enormously from edge computing. A smart home app that controls dozens of devices needs fast response times. When you tap a button to unlock your door, the command reaches an edge server that communicates directly with your smart lock, completing the action in milliseconds. This responsiveness makes the difference between a convenient smart home and a frustrating one.
The massive device density of 5G networks enables IoT mobile applications at unprecedented scale. A single 5G cell can support a million connected devices simultaneously, allowing apps to coordinate complex networks of sensors, actuators, and smart devices.
Health monitoring apps connect to multiple wearable sensors and medical devices. A cardiac patient wears sensors that track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and ECG readings. All this data streams continuously to a mobile app that analyzes patterns and alerts doctors to anomalies in real time. The app coordinates data from multiple sensors without network congestion, providing comprehensive health monitoring that was impossible when bandwidth limited the number of simultaneous connections.
Smart retail apps transform shopping experiences through sensor integration. Customers enter a store, and their mobile app connects to shelf sensors, inventory systems, smart carts, and checkout terminals. The app provides real-time product information, availability updates, personalized offers, and instant checkout. Behind the scenes, thousands of sensors track inventory levels, foot traffic patterns, temperature conditions, and equipment status. Store managers view all this data through their apps, receiving alerts when restocking is needed or when maintenance issues arise.
Logistics dashboards pull data from sensors throughout supply chains. A shipping company's mobile app tracks container locations via GPS, monitors temperature and humidity inside refrigerated containers, checks door status to prevent theft, and receives alerts about mechanical issues with trucks. Warehouse managers see real-time inventory positions. Drivers receive optimized routing based on current traffic and delivery priorities. All these data streams flow simultaneously across 5G networks without bandwidth constraints.
Manufacturing apps coordinate factory operations through sensor networks. Production managers monitor equipment status, material flow, quality metrics, and worker locations through mobile dashboards. When a machine shows signs of potential failure, the app alerts maintenance teams immediately. Cloud-based mobile apps aggregate this sensor data, apply analytics, and distribute insights to relevant personnel in seconds.
Agriculture apps connect to soil moisture sensors, weather stations, drone cameras, and automated irrigation systems. Farmers check crop health, manage water distribution, and monitor equipment from their phones. The app processes data from hundreds of sensors across large properties, providing actionable recommendations without users needing to visit every field.
5G networks make 4K and 8K streaming practical on mobile devices. Previous networks couldn't maintain consistent bandwidth for ultra-high-definition content, forcing apps to reduce quality or buffer frequently. With 5G, video apps stream high-resolution content smoothly while users move through coverage areas.
Video conferencing apps support high-quality calls with many participants. A business meeting app handles 50 participants streaming 1080p video simultaneously. Each person sees clear images of colleagues without pixelation or freezing. Screen sharing displays detailed presentations, CAD drawings, or code without compression artifacts. The high bandwidth and low latency of 5G make remote meetings genuinely comparable to in-person interactions.
Live translation capabilities become real-time. A collaboration app translates spoken words from one language to another in under a second. International teams communicate naturally, with translation happening so quickly that conversations flow normally. The app sends audio to cloud translation services over 5G connections, receives translated text or speech, and delivers results before the latency becomes noticeable.
Field service apps leverage video in new ways. A technician troubleshooting complex equipment streams live video to experts at headquarters. Those experts view high-definition footage, annotate the technician's screen to highlight specific components, and guide repairs in real time. AR/VR mobile apps on 5G enable remote assistance where experts virtually "look through" field workers' cameras and overlay instructions directly on their view.
Medical consultation apps provide specialists with high-quality video feeds during emergencies. A paramedic's app streams patient video, vital signs, and injury details to emergency room doctors. Surgeons in rural clinics consult with specialists in major hospitals, sharing surgical camera feeds in real time. The reliable, high-bandwidth connections of 5G make telemedicine genuinely effective for complex cases.
Education apps deliver immersive learning experiences through video. Students access virtual laboratories, watch 4K demonstrations of experiments, or join live lectures with hundreds of other participants. Teachers conduct interactive classes where every student's video feed remains clear regardless of how many people join. The capacity of 5G networks means educational apps can scale without compromising quality.
Mobile app architecture undergoes fundamental changes to leverage 5G capabilities and address new requirements.
Backend load shift occurs as processing moves from devices and central data centers to edge computing nodes. Traditional app architecture placed light logic on mobile devices and heavy processing in distant cloud data centers. 5G app use cases introduce a middle layer of edge servers that handle time-sensitive operations. An app might perform basic UI rendering on the device, process real-time interactions at the edge, and store long-term data in the cloud. This three-tier architecture optimizes for both speed and scalability.
Developers design apps with clear boundaries between these tiers. User interface code runs locally. Real-time features like live updates, AR overlays, and instant synchronization connect to edge servers. Analytics, user data, and historical records reside in cloud storage. This separation requires new deployment strategies and monitoring approaches.
Event-driven systems replace polling-based architectures. On 4G networks, apps frequently checked servers for updates because maintaining constant connections consumed too much battery and bandwidth. With 5G, apps establish persistent connections and receive instant notifications when changes occur. A messaging app doesn't poll for new messages every few seconds; it receives push notifications the moment messages arrive.
This shift reduces unnecessary network traffic and improves responsiveness. Apps react to events as they happen rather than discovering them during periodic checks. Financial apps update prices instantly when markets move. Social apps show new content immediately. Collaboration tools reflect changes from other users in real time.
Edge and cloud split requires developers to determine which functions belong where. Time-sensitive operations move to the edge: user authentication, content delivery, real-time analytics, and session management. Functions requiring massive computation or accessing large datasets remain in central clouds: training machine learning models, generating reports, batch processing, and long-term storage.
This distribution affects how developers structure code. Microservices architectures become more important, allowing individual functions to run on appropriate infrastructure. APIs must handle the complexity of coordinating between edge and cloud resources while presenting a simple interface to mobile apps.
API response expectations change dramatically. Users accustomed to instant responses on 5G networks won't tolerate delays. Apps must respond to interactions within 100 milliseconds or users perceive them as slow. This requirement drives developers to optimize every layer of their stack: database queries, API logic, network transmission, and UI rendering.
Developers implement predictive loading, where apps anticipate user actions and preload necessary data. Caching strategies become more sophisticated, storing frequently accessed information at multiple levels—on device, at edge nodes, and in CDN networks. Fallback mechanisms ensure apps remain functional when 5G coverage drops to 4G or slower connections.
Quality assurance for 5G applications introduces complexities that previous mobile generations didn't require.
Latency simulation becomes critical for testing. Developers must verify app behavior under different latency conditions: optimal 5G with 1ms latency, typical 5G with 10ms latency, fallback to 4G at 50ms latency, and degraded connections with 200ms or higher latency. Real-time mobile applications particularly need testing across this latency spectrum to ensure they degrade gracefully rather than failing completely.
Testing tools must simulate network conditions accurately. A QA team might test a video conferencing app under various scenarios: perfect 5G connectivity, intermittent connection drops, transitions between 5G and 4G, and bandwidth throttling during network congestion. Each scenario reveals different bugs and performance issues.
Load variability requires testing apps under fluctuating network conditions. 5G bandwidth varies based on user density, physical obstacles, weather conditions, and distance from towers. An app that works perfectly with consistent 1 Gbps connections might fail when bandwidth drops to 100 Mbps or fluctuates rapidly. QA processes must include scenarios where network performance changes dramatically within seconds.
Edge computing introduces additional variables. Apps relying on edge servers need testing for edge node failures, routing changes, and synchronization issues between edge and cloud resources. When an edge server goes offline, does the app fall back to cloud resources gracefully? Does data remain consistent across edge and cloud storage?
Device density testing verifies app performance when many users connect simultaneously. IoT mobile applications coordinating hundreds or thousands of sensors need testing at scale. A smart building app might work fine with 50 connected devices but fail when managing 500. Load testing must simulate realistic device densities and interaction patterns.
S3Corp addresses these testing challenges through specialized QA automation frameworks. The company builds testing environments that simulate various 5G network conditions, allowing clients to identify issues before deployment. Automated testing pipelines verify app performance across latency ranges, bandwidth variations, and device densities. This approach catches problems that manual testing might miss.
S3Corp develops mobile applications that fully utilize 5G technology while maintaining reliability across different network conditions. The company's approach combines technical expertise with practical understanding of client needs across multiple industries.
Application development at S3Corp starts with architecture design that accounts for 5G capabilities. Development teams structure apps to leverage edge computing, implement low-latency app architecture, and prepare for future 5G features. Engineers consider where processing should occur—on device, at edge nodes, or in cloud infrastructure—based on latency requirements, computational intensity, and data sensitivity.
For fintech clients, S3Corp builds trading platforms that execute transactions in milliseconds. These apps connect to edge servers for real-time market data and order execution while maintaining secure connections to central banking systems for settlement and compliance. The architecture ensures traders receive instant feedback on their actions while meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Healthcare applications from S3Corp integrate with medical devices and sensors over 5G networks. Patient monitoring apps collect data from multiple wearables, process information at edge servers to detect anomalies, and alert medical staff within seconds of identifying potential issues. Telemedicine platforms stream high-quality video for consultations while protecting patient privacy through encrypted connections.
Retail applications leverage IoT mobile applications to coordinate inventory systems, point-of-sale terminals, customer apps, and backend systems. S3Corp builds solutions where customers receive personalized offers on their phones as they browse stores, checkout happens automatically as customers leave, and inventory updates occur in real time across all channels.
Telecom clients work with S3Corp to develop network management apps that monitor 5G infrastructure. These applications track tower performance, device connections, bandwidth usage, and service quality across entire networks. Engineers view real-time dashboards on mobile devices, receiving alerts about issues before customers notice problems.
QA automation ensures S3Corp applications perform reliably under varying conditions. The company develops custom testing frameworks that simulate different network scenarios: optimal 5G, degraded 5G, 4G fallback, and complete connection loss. Automated tests verify that apps maintain functionality across this spectrum, degrading gracefully when network quality decreases rather than crashing or freezing.
Testing covers performance under load, security against network-based attacks, compatibility across device types, and integration with edge computing infrastructure. S3Corp tests apps on actual 5G networks in different markets, accounting for variations in network implementation between carriers and countries.
DevOps and monitoring systems track app performance in production. S3Corp implements monitoring that measures actual latency, bandwidth usage, edge server response times, and user experience metrics. When issues arise, automated alerts notify development teams immediately. Analytics help identify performance bottlenecks, whether they occur in app code, edge infrastructure, or network connectivity.
The company maintains continuous integration and deployment pipelines that allow rapid updates to applications. When 5G networks add new features or capabilities, S3Corp quickly adapts client apps to take advantage of improvements. This agility ensures applications remain competitive as technology evolves.
S3Corp combines these services into comprehensive partnerships with clients. Rather than simply building apps, the company provides ongoing expertise in 5G mobile app development, helping clients understand which use cases benefit most from 5G capabilities and how to implement solutions effectively.
The transformation that 5G brings extends far beyond faster smartphone downloads. This technology enables genuinely new capabilities across industries and daily life—from surgery performed across continents to cars that communicate to prevent accidents, from immersive entertainment that feels real to business collaboration that transcends physical distance.
We're still in the early stages. As 5G infrastructure deployment continues and developers, businesses, and entrepreneurs discover what becomes possible with this foundation, applications we haven't yet imagined will emerge. The pattern repeats with each technological leap: the most transformative uses aren't obvious at launch. No one predicted social media would reshape politics when smartphones first appeared. Similarly, the most significant impact of 5G likely hasn't been invented yet.
What's clear is that 5G network technology represents critical infrastructure for the digital economy. Countries, cities, and businesses that invest in deployment position themselves for competitive advantage. Those that lag risk being left behind as commerce, communication, and essential services increasingly depend on high-speed, low-latency connectivity.
The future of software development increasingly incorporates 5G capabilities from conception rather than retrofitting them afterward. Developers who understand how to leverage 5G speed, low latency, and massive device support will create the applications that define the next decade of digital innovation. As technology continues to evolve, forward-thinking organizations like S3Corp. are already preparing for what comes next: integrating 5G with AI, edge computing, and IoT to build smarter, faster, and more responsive digital ecosystems.
5G operates on higher frequency bands that carry more data simultaneously. Networks achieve speeds of 10-20 Gbps compared to 4G's maximum of about 1 Gbps. This bandwidth allows apps to download large files instantly, stream high-resolution video without buffering, and sync data across devices in real time.
Network latency decreases from about 50 milliseconds on 4G to as low as 1 millisecond on 5G. This improvement comes from more efficient radio technology, better network architecture, and edge computing infrastructure that processes requests closer to users. Lower latency makes apps respond instantly to user actions.
No. Simple apps like calculators, note-taking tools, or offline games gain little from 5G. Apps that benefit most include real-time multiplayer games, augmented reality experiences, video streaming services, IoT device controllers, and professional tools requiring instant data synchronization. Developers should evaluate whether their specific use case justifies 5G optimization.
Edge computing places processing power at network edges—regional data centers or cell tower locations—rather than distant cloud facilities. Apps send requests to nearby edge servers that respond in milliseconds. This architecture reduces latency for time-sensitive operations while maintaining access to cloud resources for tasks that don't require instant responses.
Yes, with proper design. Developers build apps that detect available network speeds and adjust functionality accordingly. On 5G, apps enable advanced features like real-time AR or 4K streaming. On 4G, the same apps reduce quality, disable bandwidth-intensive features, or use local processing instead of cloud services.
Results vary by implementation. Apps that offload heavy processing to edge or cloud servers can reduce battery consumption because phones do less computational work. However, 5G radios consume more power than 4G when actively transmitting. Well-designed apps balance these factors, using 5G bandwidth efficiently and minimizing unnecessary data transmission.
Healthcare gains remote patient monitoring and telemedicine capabilities. Manufacturing uses apps to coordinate IoT sensors across factories. Retail implements seamless shopping experiences with smart stores. Finance builds trading platforms with millisecond execution. Entertainment delivers immersive AR/VR experiences. Transportation coordinates autonomous vehicles and smart traffic systems.
Testing requires simulating various network conditions: optimal 5G, degraded 5G, transitions to 4G, and poor connectivity. Developers use specialized tools to control latency, bandwidth, and packet loss during testing. Load testing verifies performance with many simultaneous users or connected devices. Testing on actual 5G networks in different locations ensures apps work across carrier implementations.
Whether you have any questions, or wish to get a quote for your project, or require further information about what we can offer you, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Contact us Need a reliable software development partner?
S3Corp. offers comprehensive software development outsourcing services ranging from software development to software verification and maintenance for a wide variety of industries and technologies
Software Development Center
Headquater 307
307/12 Nguyen Van Troi, Tan Son Hoa Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Office 146
3rd floor, SFC Building, 146E Nguyen Dinh Chinh, Phu Nhuan Ward, HCMC
Tien Giang (Branch)
1st floor, Zone C, Mekong Innovation Technology Park - Tan My Chanh Commune, My Phong Ward, Dong Thap Province
_1746790910898.webp?w=384&q=75)
_1746790956049.webp?w=384&q=75)
_1746790970871.webp?w=384&q=75)
